BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH). PROSTATE CANCER AND PROSTATITIS: THE EMERGING EMERGENCY IN THE DISTORTION OF MEN'S SEXUAL ...
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH). PROSTATE CANCER AND PROSTATITIS: THE EMERGING EMERGENCY IN THE DISTORTION OF MEN’S SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH; THE PROGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT.
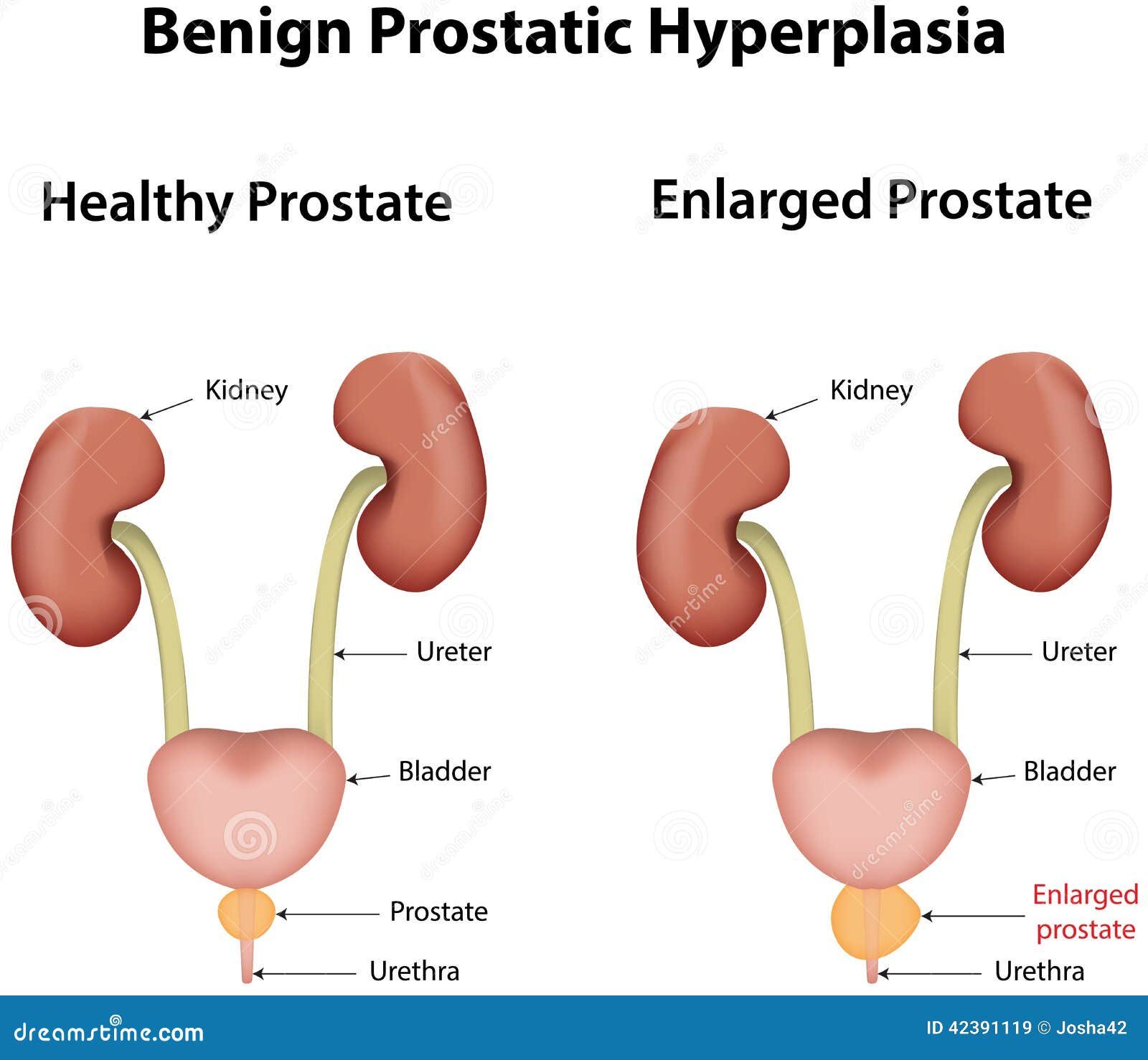
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY
The prostrate is a gland below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is shaped like a walnut. Its main function is to add and concentrate seminal fluid and the muscle helps to push semen through the urethra.
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is the proliferation and abnormal multiplication of cellular elements of the prostate gland.
The consequences of this is chronic bladder outlet-obstruction due to pressure of the enlarged prostate on the urethra and the bladder.
This leads to stricture of the urethra causing difficulty in passing urine in males which in turn leads to urinary retention, pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis in the kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections haematuria and bladder calculi.
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF BPH
- Hesitancy: difficulty in initiating the urinary stream.
- Urinary frequency: the urge to pass urine every 2 hours.
- Intermittency: the urge to stop and start several times when passing urine.
- Urgency: feeling the urgent need to pass urine as if you cannot wait.
- Weak urinary stream: weak urine flow.
- Straining: trouble starting to pass urine.
- Nocturia: the need to wake up more than 2 times to pass urine at night.
MEN AT RISK FOR BPH
- Men over the age of 50 years, as the risk of BPH rises with age.
- Men whose father had BPH.
- Men who are overweight or obese.
- Men that do not exercise.
- Some men with erectile dysfunction.
Common disorder that affect the prostate
- Inflammation – prostatitis
- This is caused by either chronic or acute bacteria infection.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) this is the enlargement of the prostate gland with advancing age. The enlarged prostate may grow to block the urethra making it difficult to pass both urine and faecal matter.
- Prostate cancer: this occurs when the prostate proliferates with cancer cells that may metastasize and cause very serious problem to adjoining organs.
- Erectile dysfunction
- Blood in the urine/semen heamatospermia
- Pain in the lower back, hip or chest.
HOW TO KEEP THE PROSTATE HEALTHY
- Getting regular prostate screening from the age of 50 or earlier if there is a family history of prostate cancer.
- Exercising regularly: people who are more physically active are less likely to have BPH.
- Eating healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables and healthy protein.
- Quitting smoking.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE PROSTATE DISORDERS
- Digital rectal examinations:
The doctor inserting with a gloved hand the index finger through the rectum to feel the prostate. - Ultra sound: using trans-abdominal/ transcretal view to Image the prostate gland.
- PSA: Prostate Specific Antigen is a protein produced by the prostrate and found mostly in semen with very small amounts released into the blood stream. Sometimes prostate gland may release slightly high PSA for other reasons. The PSA is the leading test of prostate cancer screening. PSA screening can help detect cancer at an early stage when treatment may be more effective with potentially fewer side effects.
PROSTATE CANCER SURVIVAL RATES
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer in the US including skin cancer and the second leading cancer in men worldwide 1 in 8 US men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point in their lives. Prostate cancer incidence increases with age.
Although only about 1 in 456 men under the age of 50 will be diagnosed, the rate shoots up to 1 in 54 for ages 50-59. 1 in 11 for 70 years and above. Nearly 60% of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men over the age of 65.
The diagnosis of prostate cancer is by Biopsy which is necessitated by elevated serum PSA levels. While prostate cancer is relatively common the good news is that more than 80% of all prostate cancers are detected when the cancer is confined to the prostrate and areas around it, and treatment success rates are high compared with many other types of cancer.
The 5-year survival rate in the United States for men diagnosed with early stage prostate cancer is greater than 99%. In other words the chance of a man dying from prostate cancer is low especially when detected early.
Amidst so much optimism and progress in the last 10 years. It is important to keep in mind that prostate cancer is still a deadly disease for some men and it is the second leading cause of cancer death among men in US, with 94 men dying from it daily.
In general, the earlier the cancer is detected and treated the more likely the survival, infact many men with “low risk” tumors (which are the most common type of prostate cancer) as well as men with intermediate risk disease can safely undergo active surveillance; This means patient are closely monitored without immediate treatment for treatment related side effects while still preserving their chance of long term-survival if the cancer becomes aggressive enough to require treatment.
ESTABLISHED RISK FACTORS
Racial background, family history and age. Other risk factors include smoking, obesity and consumption of high amount of calcium.
Men of African descend are 1.6 times more likely to get prostate cancer and more than twice as likely to die from it.
Diagnosis of BPH is by transcretal ultrasound scan which is the gold standard where prostrate volume is measured L x W x H x 0.523 (volume of ellipsoid).
BPH > 40ml in male adults above 60 years
Drugs Can Shrink Prostate Includes:
Tansulosin (Flomax) or Terazosin (Hytrin) which relax muscle tissues. Avodartad and Finasteride (Proscar). A combination of the 2 when used for a long term may be useful
* Alpha blockers work by relaxing the smooth muscle of the bladder neck and prostate gland. This makes peeing easier.
Alpha blockers include Affuzasin (Uroxatral) Doxazosin cardula. This often work quickly in people with small prostates.
Active sexual activity has been shown not to have effect on the incidence of BPH.
There is no evidence that BPH can alter sexual functions.
However many treatments for BPH do cause problems like erectile dysfunction and ejaculation and changes in libido.
There is no evidence having frequent ejaculations can shrink your prostate. Having prostate enlargement does not mean you will have prostate cancer.
Finally, it is advised that men from the age of 40 shall undertake prostate specific antigen screening every 2 years and yearly from 50 with transrectal scan. From 60 years twice yearly so as to increase the chance of early detection and management.
At Pioneer Medical Diagnostic Clinic, we are dedicated to providing accurate and reliable diagnostic testing to support patient care. With state-of-the-art technology and a team of experienced professionals, we offer a comprehensive range of medical diagnostic services, ensuring timely and precise results.